Overall Solution for Large-scale Production of High-quality 3D Exosomes
- Categories:Company News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2022-07-05
- Views:0
(Summary description)【Introduction】
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are promising candidates for the treatment of chronic degenerative diseases. These cells can regenerate or differentiate into other cell types, and secrete various trophic factors to participate in migration, proliferation, and immunomodulation. However, this treatment still faces some unresolved challenges. A common issue is the low survivability and migration of systemically infused MSC towards targeted regions. Nevertheless, successful clinical treatment of various chronic diseases suggests that the MSCs may have an alternative mechanism. In a recent review published in Am J Transl Res, researchers from University Kebangsaan Malaysia summarized the biodistribution of MSCs in animal models following systemic injection, revealing the potential role of exosomes in MSC therapy.
Overall Solution for Large-scale Production of High-quality 3D Exosomes
(Summary description)【Introduction】
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are promising candidates for the treatment of chronic degenerative diseases. These cells can regenerate or differentiate into other cell types, and secrete various trophic factors to participate in migration, proliferation, and immunomodulation. However, this treatment still faces some unresolved challenges. A common issue is the low survivability and migration of systemically infused MSC towards targeted regions. Nevertheless, successful clinical treatment of various chronic diseases suggests that the MSCs may have an alternative mechanism. In a recent review published in Am J Transl Res, researchers from University Kebangsaan Malaysia summarized the biodistribution of MSCs in animal models following systemic injection, revealing the potential role of exosomes in MSC therapy.
- Categories:Company News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2022-07-05
- Views:0
【Introduction】
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are promising candidates for the treatment of chronic degenerative diseases. These cells can regenerate or differentiate into other cell types, and secrete various trophic factors to participate in migration, proliferation, and immunomodulation. However, this treatment still faces some unresolved challenges. A common issue is the low survivability and migration of systemically infused MSC towards targeted regions. Nevertheless, successful clinical treatment of various chronic diseases suggests that the MSCs may have an alternative mechanism. In a recent review published in Am J Transl Res, researchers from University Kebangsaan Malaysia summarized the biodistribution of MSCs in animal models following systemic injection, revealing the potential role of exosomes in MSC therapy.
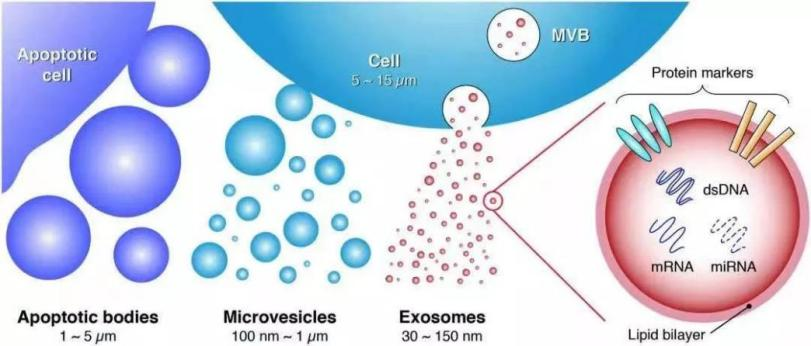
Figure 1 | Classification of extracellular vesicles
Exosomes carry a variety of proteins, mRNAs, miRNAs, and lipids, and are widely involved in intercellular material transport and information transmission, as well as regulation of physiological and pathological processes [2]. First, due to the small size of exosomes, these nanoparticles can easily traverse the intercellular space of regular capillaries and are therefore highly effective. Secondly, the outer membrane of exosomes presents few antigens which are difficult to recognize by the immune system and do not cause immune rejection; therefore, exosomes are increasingly used in clinical research.
Currently, 258 clinical trials related to exosome therapy and diagnosis have been conducted worldwide for indications such as GvHD, macular fissure, severe COVID-19 pneumonia, and diabetes mellitus. In addition, exosomes can be used as "natural nanoparticles" for drug delivery [3].
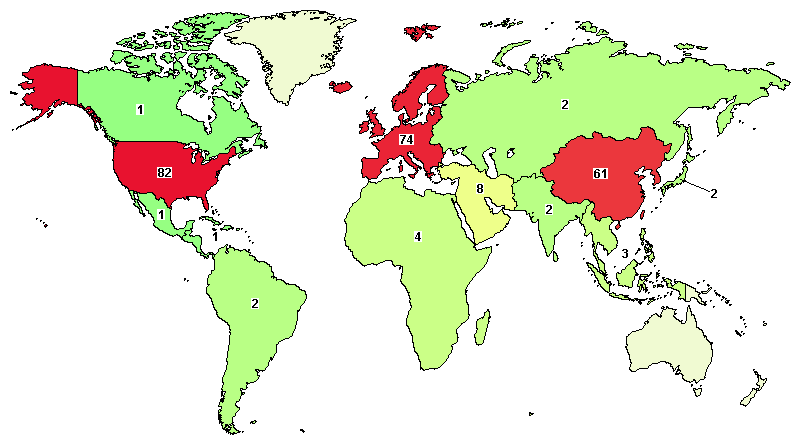
Figure 2 | Global distribution of exosome clinical trials
Image source: https://ClinicalTrials.gov
【Key Points for Commercialization of Exosomes】
In recent years, two key factors have contributed to the effective introduction of exosome therapy to the market and its subsequent commercialization.
1. "Quality" of exosomes
In clinical studies, the quality of exosomes is crucial to their efficacy, hence the quality of cells secreting exosomes is of particular importance. 3D cell culture simulates the growth environment in vivo, providing a more suitable three-dimensional environment for cell growth. The growth condition of cells can be observed at any time during the 3D culture to ensure high cell viability while collecting exosomes secreted by cells.
2. "Quantity" of exosomes
The stable, economical, and efficient manufacturing process is also crucial for exosome production on a large scale. Harvesting exosomes suitable for clinical research may take weeks using the conventional 2D culture + ultracentrifugation method. It is preferrable to ensure exosome quality while achieving automated, large-scale collection of exosomes from cell supernatants within one day. CytoNiche can provide a complete set of solutions for exosome production and purification.
【Total Solution for 3D FloTrix® Exosome Production and Purification】
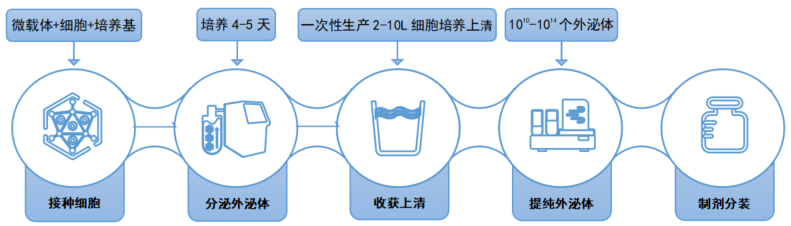
Figure 3 | Flow chart of exosome production and purification
Stage 1: Large-scale 3D cell culture
✦ Cells: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSC)
✦ Micro-carriers: 3D TableTrix® Stem Cell Micro-carrier Tablets W Series Type S (W02)
✦ Medium: 3D FloTrix® Cell Culture Medium (RMZ010-DW)
✦ Culture vessels: 3D FloTrix® vivaSPIN VS Series Automated Bioreactor (FTVS10)
✦ 3D cell culture cycle: 5 days
✦ Culture results: 10 L of cell culture supernatant collected at one time
✦ Cell growth condition:
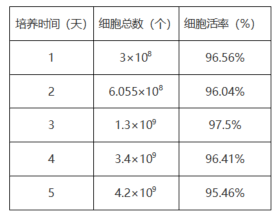
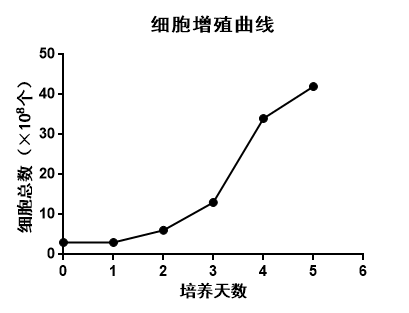
Table 1 Figure 4|Cell proliferation curve
Stage 2: Exosome concentration and harvesting
✦ Cell culture supernatant: 10 L of 3D cell culture supernatant
✦ Purification equipment: 3D FloTrix® vivaEXO Exosome Harvesting System
✦ Purification principle: Clarification + concentration via multi-stage filtration system to harvest and enrich exosomes in cell culture supernatants.
✦ Methods of use: Disposable tubing consumable kit can be used together with the vivaEXO Exosome Harvesting System. By connecting the outlet tubing of the vivaSPIN bioreactor to the inlet tubing of the vivaEXO Exosome Harvesting System, a fully enclosed, seamless connection of "culture-harvesting" can be achieved.
✦ Collection time: 10 L of cell culture supernatant is concentrated and enriched 20-fold in only 1–3 h (depending on the viscosity of the culture medium)
✦ Purification results: 500 mL of highly concentrated, sterile exosome solution is collected
Stage 3: Exosome identification
1) Determine the concentration and particle size range of exosomes using Nanoparticle Tracking analyzer (NTA):
The concentration of exosome particles is 5.7 × 1011 particles/mL, the total number of particles is 2.85 × 1014 particles, with an average particle size of 135 nm after NTA testing.
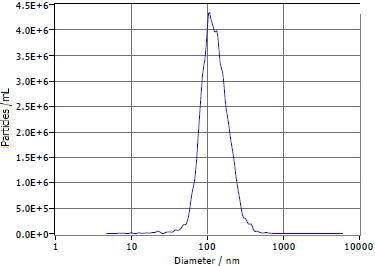
Figure 5 | Exosome particle size range
2) Detect the expression of 3D exosome surface markers by Western blot (WB):
Positive surface markers on exosomes: TSG101 and CD63 show clear bands, and the negative surface marker Calnexin is not expressed.
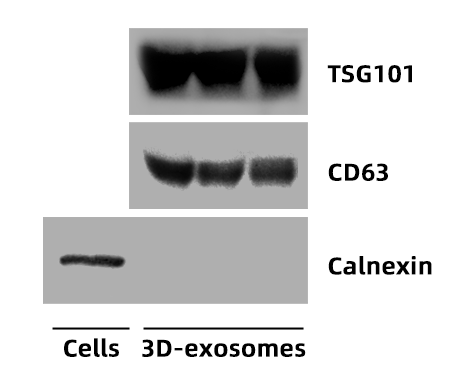
Figure 6 | WB identification results
3) Observe the 3D structure of exosomes by transmission electron microscopy (TEM):
A classical "cup-and-disc" structure of the exosome is observed by TEM.
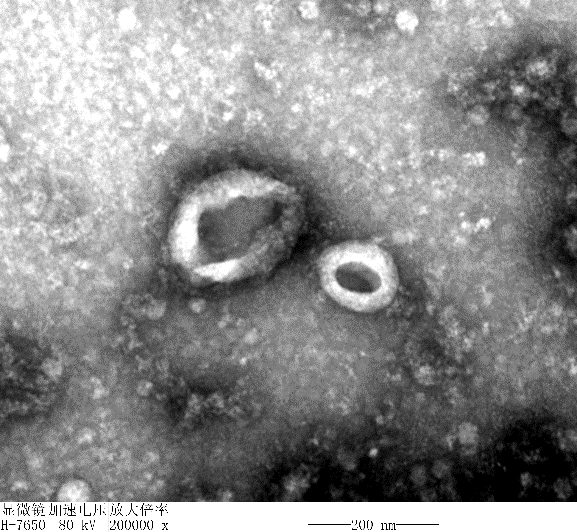
Figure 7 | Exosome structure
【Examples of Exosome Applications】
1. Therapeutic exosomes as drugs
Due to their abundance of bioactive substances, exosomes have an inherent therapeutic potential and are used in the field of medical regeneration for repair and regeneration of different tissues. The clinical studies of exosomes include the cardiovascular system, endocrine metabolic system, etc. In addition to the above areas, stem cell-derived exosomes are used in a variety of disease areas, such as diabetes, osteoarthritis, repair of endometrial injury, and cancer.
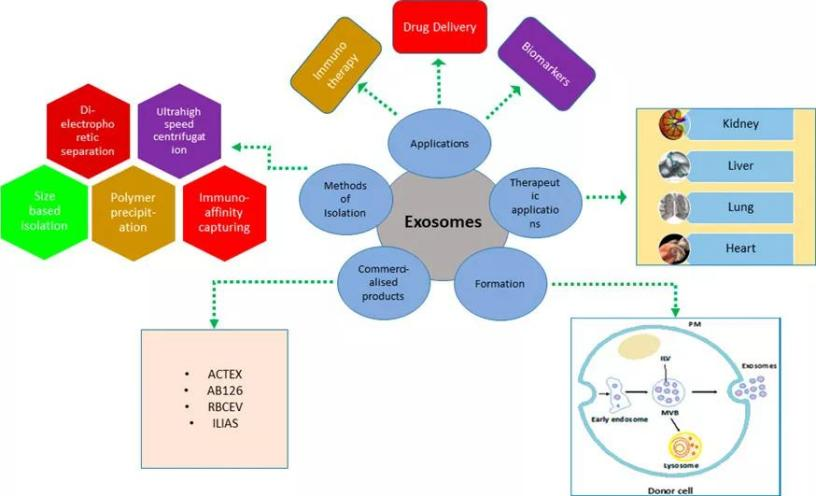
Figure 8 | Exosome applications
First, exosomes can facilitate cell repair and regeneration. The three main causes of aging are cell injury, cell malnutrition, and cell inactivation. Therefore, promoting cell regeneration is the key to anti-aging [4]. Exosomes are able to remotely target and regulate cell repair, growth, and differentiation, effectively inhibiting cellular aging. They can effectively transfer nutrients into cells, participate in cell renewal, condition skin, improve skin texture, and restore skin to a youthful, healthy state.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were cultured using different methods (2D, 3D), and the secreted exosomes were collected for cell proliferation assays. The cells (MSC) were cultured by adding different concentrations of exosomes to the basal medium for 4 days, and the cell proliferation was detected using the CCK-8 kit. As shown in Figure 9, both 2D- and 3D-exosomes could promote cell proliferation, with 3D-exosomes having a more pronounced effect on cell proliferation than 2D-exosomes.
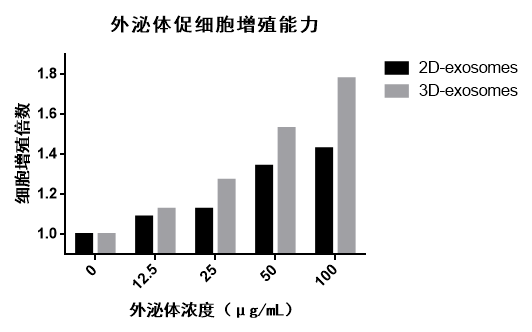
Figure 9 | The proliferation folds of cells promoted by 2D- and 3D-exosomes
Moreover, exosomes can promote fibroblast proliferation. Fibroblasts are the master cell population in the dermis of skin, and their health and activities are critical to the skin health and beauty. Exosomes can enhance the proliferative capacity of fibroblasts, thereby reversing aging of fibroblast.
Likewise, MSCs were cultured using different methods (2D, 3D), and the secreted exosomes were collected for fibroblast proliferation assays. Fibroblasts in Group 1 (Figure 10) and Group 2 (Figure 11) were cultured by adding different concentrations of exosomes, and the cell proliferation was detected using the CCK-8 kit. In two sets of experiments, both 2D-exosomes and 3D-exosomes could promote the proliferation of fibroblasts, with 3D-exosomes having a more pronounced effect on fibroblast proliferation than 2D-exosomes. As the exosome concentration increased, the proliferation-promoting capability decreased, and the exosomes showed a better proliferation-promoting effect at a concentration of 25 μg/mL.
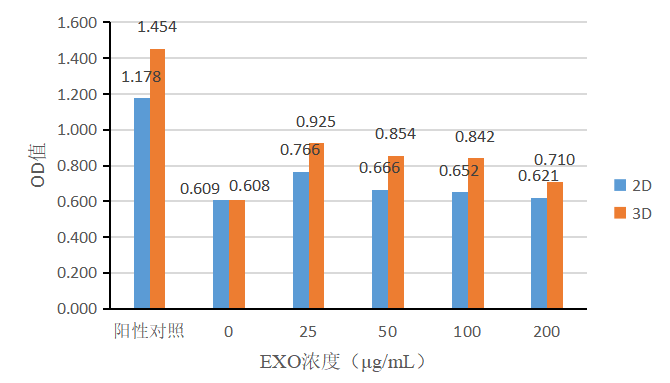
Figure 10 | Effect of basal medium + various concentrations of exosomes on the proliferation of fibroblasts
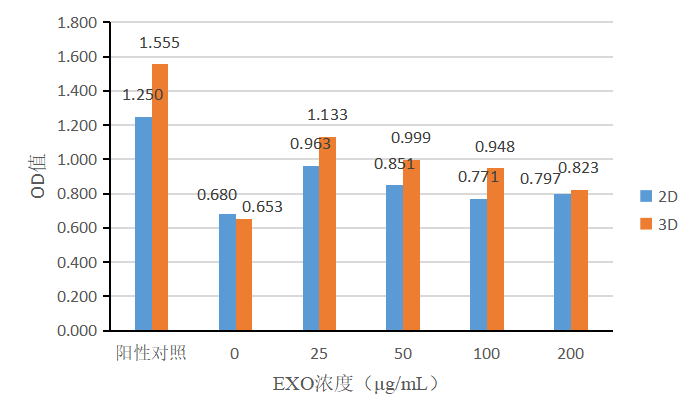
Figure 11 | Effect of medium containing 1% FBS + various concentrations of exosomes on the proliferation of fibroblasts
2. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles
As "naturally domesticated" endogenous nanocarriers, exosomes can carry RNA, DNA, proteins, and other signaling molecules, and maintain the biological activity of their contents in vivo. Featuring low immunogenicity and high safety, exosomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for therapeutic biomolecules. For example, exosomes can be used as delivery vehicles for therapeutic nucleic acid drugs, delivering mRNA, miRNA, etc., to target cells, thereby regulating the expression of target genes for therapeutic purposes.
The same number of engineered cells cultured using different culture methods (2D, 3D) were seeded (2D cells are seeded at a density of 1 × 106 cells/mL in 10 mL of medium; 3D cells are seeded at a density of 5 × 105 cells/mL in 20 mL of medium), and cell culture supernatants were collected at different time after 3D culturing. The total number of 3D-exosomes secreted by the harvested engineered cells was higher than that of 2D-exosomes, and the amount of exosomes secreted increased with increasing 3D culture time. Figure 12 shows the total number of exosome particles secreted using different culture methods (2D/3D) and with different culture times.
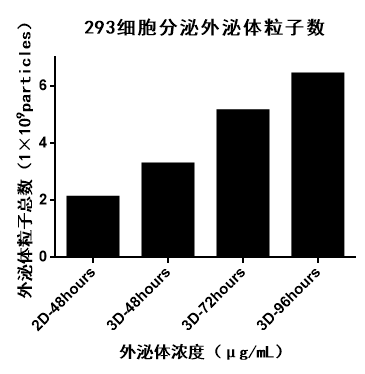
Figure 12 | Total number of exosome particles
Exosomes harvested in 3D culture exhibited a higher level of "quality" and "quantity" than exosomes harvested in 2D culture, both as therapeutic drugs and as drug delivery vehicles. The 3D culture method offered by CytoNiche also provides more opportunities for experts in the field of exosome-related research. We look forward to cooperating with more enthusiasts in this field to explore the new world of 3D exosomes.
【Technical Services】
CytoNiche can also provide the appropriate technical services for diverse directions and nodes for cell culture and collection.
1. Service items
✦ Cell supernatant production service: Mass production of stem cells and engineered cell culture supernatant;
✦ Exosome purification service: Exosome purification from cell supernatants;
✦ Quality testing service: Detection of microbes, endotoxin, mycoplasma, protein concentration, cell secreted factors, etc., in cell supernatant. Identification of exosomes by particle concentration, particle size, transmission electron microscopy, and Western blot.
2. Service content
✦ Provide customized experimental protocols;
✦ Customize 3D cell culture and cell derivative collection;
✦ Optimize 3D cell culture process.
【References】
[1] Breakefield X.O., Frederickson R.M., Simpson R.J. Gesicles: Microvesicle “cookies” for transient information transfer between cells. Mol. Ther. 2011; 9:1574–1576.
[2] Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 7;15(3):4142-57.
[3] Ha D, Yang N, Nadithe V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016 Jul;6(4):287-96.
[4] Ha DH, Kim HK, Lee J, Kwon HH, Park GH, Yang SH, Jung JY, Choi H, Lee JH, Sung S, Yi YW, Cho BS. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells. 2020 May 7;9(5):1157.

Please feel free to contact us with your questions and needs, and our technicians will communicate with you in detail.
There is also a chance to receive an exquisite gift!
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
-
Phone
- Service hotline+86 400-012-6688
-
E-mail
- E-mailwangal@cytoniche.com
- TOP


 京公网安备 11010802037749号
京公网安备 11010802037749号
