[Review] Exosomes with Big Roles in Cancer, Vaccine Development, and Therapeutics[Review] Exosomes with Big Roles in Cancer, Vaccine Development, and Therapeutics[Review] Exosomes with Big Roles in Cancer, Vaccine Development, and Therapeutics[Review] Exos
- Categories:Company News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2022-06-22
- Views:0
(Summary description)[Introduction] Cancerisadeadlydiseasethatisgloballyoneoftheleadingcausesofmortalityeveryyear.Despitetheavailabilityofchemotherapy,radiotherapy,immunotherapy,andsurgery,acureforcancerhasnotbeenattained
[Review] Exosomes with Big Roles in Cancer, Vaccine Development, and Therapeutics[Review] Exosomes with Big Roles in Cancer, Vaccine Development, and Therapeutics[Review] Exosomes with Big Roles in Cancer, Vaccine Development, and Therapeutics[Review] Exos
(Summary description)[Introduction] Cancerisadeadlydiseasethatisgloballyoneoftheleadingcausesofmortalityeveryyear.Despitetheavailabilityofchemotherapy,radiotherapy,immunotherapy,andsurgery,acureforcancerhasnotbeenattained
- Categories:Company News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2022-06-22
- Views:0
[Introduction]
Cancer is a deadly disease that is globally one of the leading causes of mortality every year. Despite the availability of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and surgery, a cure for cancer has not been attained. Recently, exosomes have gained significant attention due to their potential in cancer treatment. Researchers from the University of Chicago and Campinas University in Brazil jointly published a review article on Bioactive Materials, introducing the significance of various components of exosomes in the malignant progression of cancer, and summarizing the potential of exosomes as vaccines and delivery carriers in cancer treatment.
[Review]
xosomes are extracellular vesicles that are released by the endosomes of cells via exocytosis and have been previously considered as the "waste" in cells. However, a growing number of studies now consider them crucial to intercellular communication and key players in different physiological and pathological processes including cancer. Exosomes are engaged in tumor microenvironment functions such as induction of angiogenesis, cell migration and proliferation, inflammatory responses, immune suppression, escape from immune surveillance, and metastasis. Exosomes ensure cellular communication within the microenvironment, modify the recipient cell phenotype to be tumorigenic, and promote primary tumor growth by transferring multiple types of "cargo" to stroma cells, such as proteins, lipids, enzymes, transcription factors, DNA, mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs,.
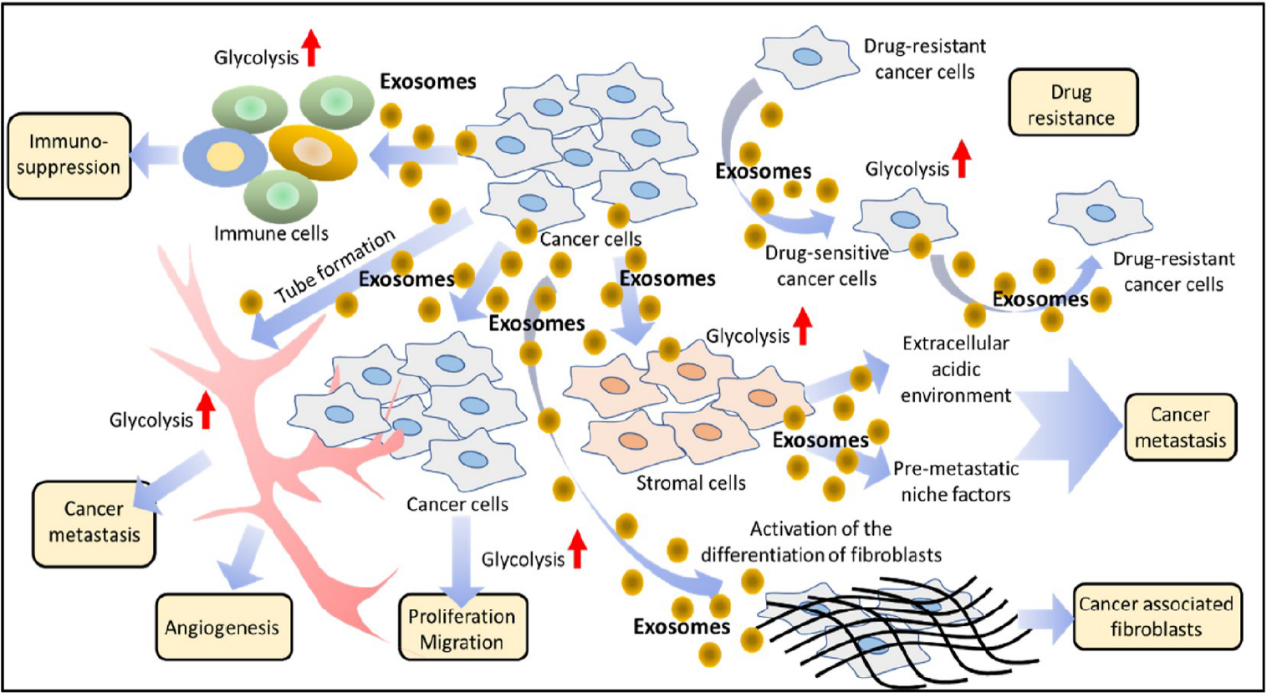
Figure | Modulation of various events in the tumor microenvironment via exosomal communication
Most pathological events, including cancer, that occur via exosomes involve two major processes: release of exosomes from donor cells and their uptake by recipient cells. Therefore, blocking or inhibiting the release or uptake of exosomes may be a means by which to inhibit metastasis or malignant progression of cancer.
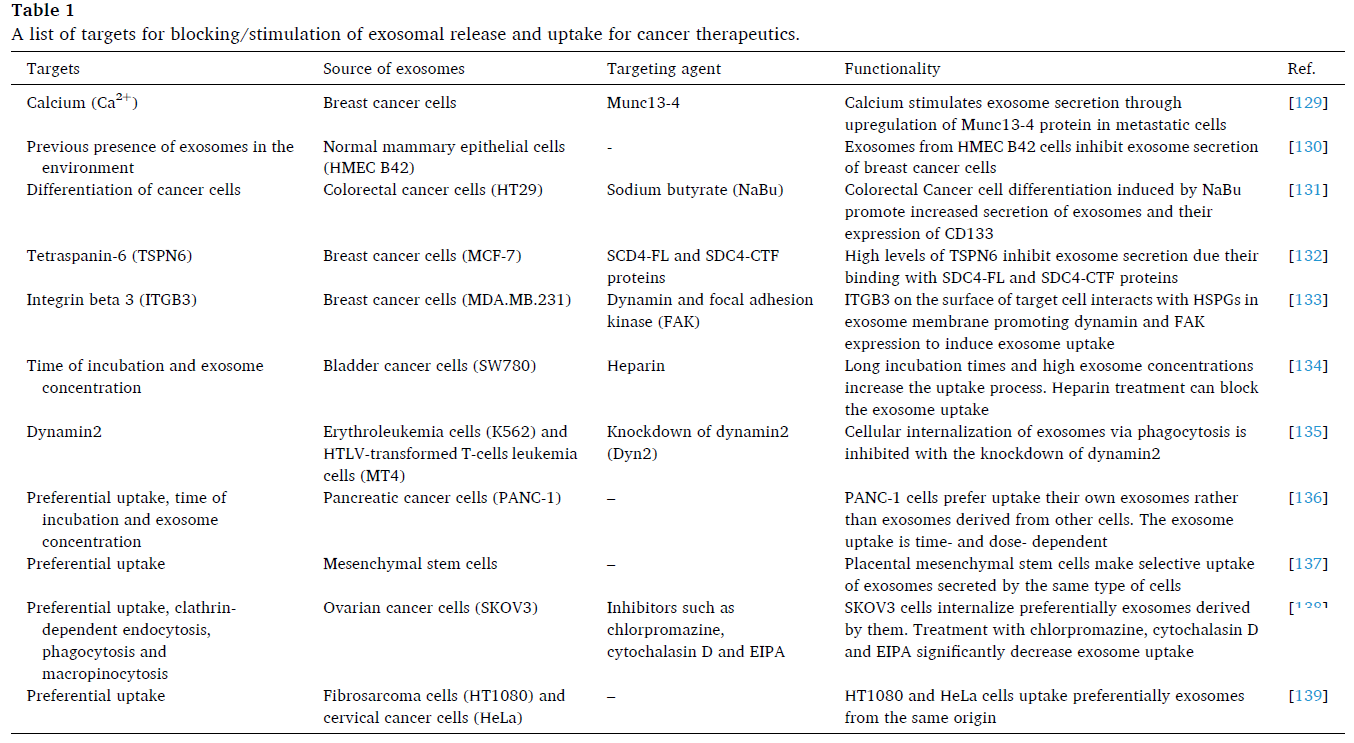
Figure | A list of targets for blocking/stimulation of exosomal release and uptake for cancer therapeutics
In addition, recent studies have shown that exosomes have great potential for cancer immunotherapy and can be used as effective vaccines against cancer. B cells release exosomes, which carry MHC class II peptide complexes, facilitating the antigen presentation to primed CD4+ T cells. Dendritic cells release exosomes that carry MHC class I or MHC class II peptide complexes, facilitating antigen recognition of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Macrophages release exosomes that carry antigens related to pathogens, facilitating the dendritic cell maturation and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Notably, although tumor-derived exosomes can produce an anti-tumor response, they can also cause immunosuppression and hinder cancer immunotherapy. Therefore, it is crucial to decipher the immune-stimulating mechanism of exosomes so that they can be utilized as a carrier of antigens and adjuvants of cancer vaccines.
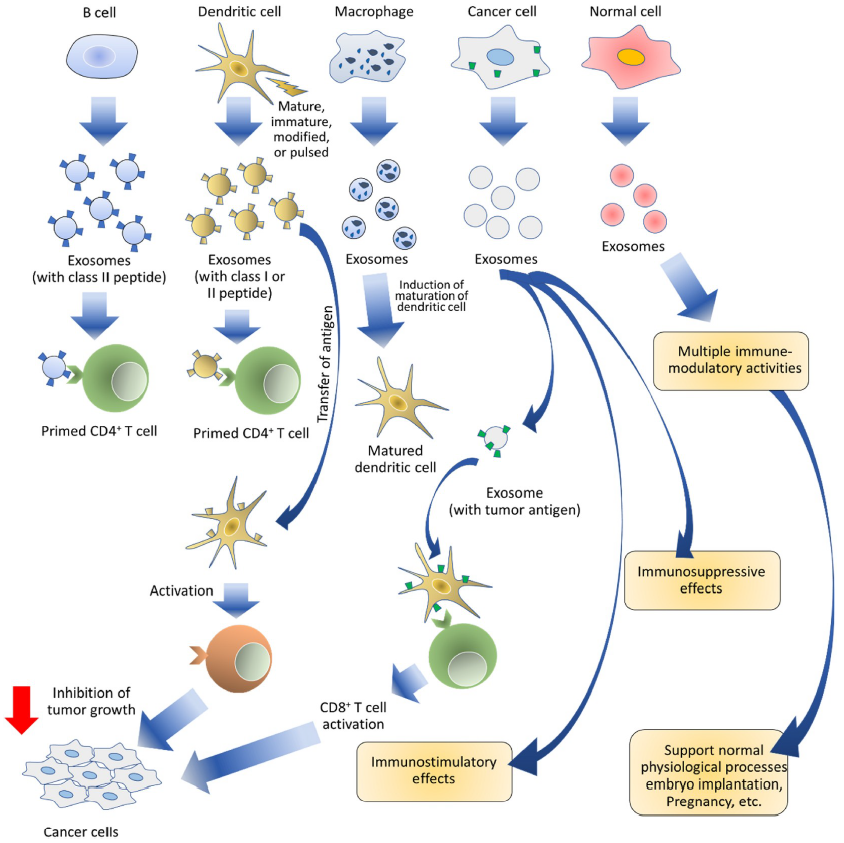
Figure | Potential applications of exosomes in immunotherapy and cancer vaccines
As a novel approach to the targeted therapy of cancer, drug delivery systems (DDSs) have multiple advantages such as controlled composition, high loading capacity, large scale production, and low cost. However, the application of synthetic DDSs as therapeutics is hampered by several factors, including adverse immunogenic reactions, toxicity, low biocompatibility, and promotion of coagulation, inflammation, and endothelium damage. Recently, several studies have proposed the use of exosomes as potential DDSs for therapeutic application in cancer. Featuring small size, high stability, excellent biocompatibility, and good safety profile, exosomes can be used as efficient tumor-targeting vehicles to transport drugs to nearby or distant cells.
Exosomes can be administered via intravenous, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, intranasal, and oral routes. Moreover, drug molecules can be loaded into exosomes in various ways, such as pre-loading and post-loading approaches, which occur during exosome biogenesis and after exosome isolation, respectively. In the pre-loading approach, therapeutic molecules are packaged into cells via transfection, co-incubation, or genetic engineering, and then are loaded into exosomes produced by them. In contrast, the post-loading approach involves the incorporation of the drug molecules directly into the processed exosomes.
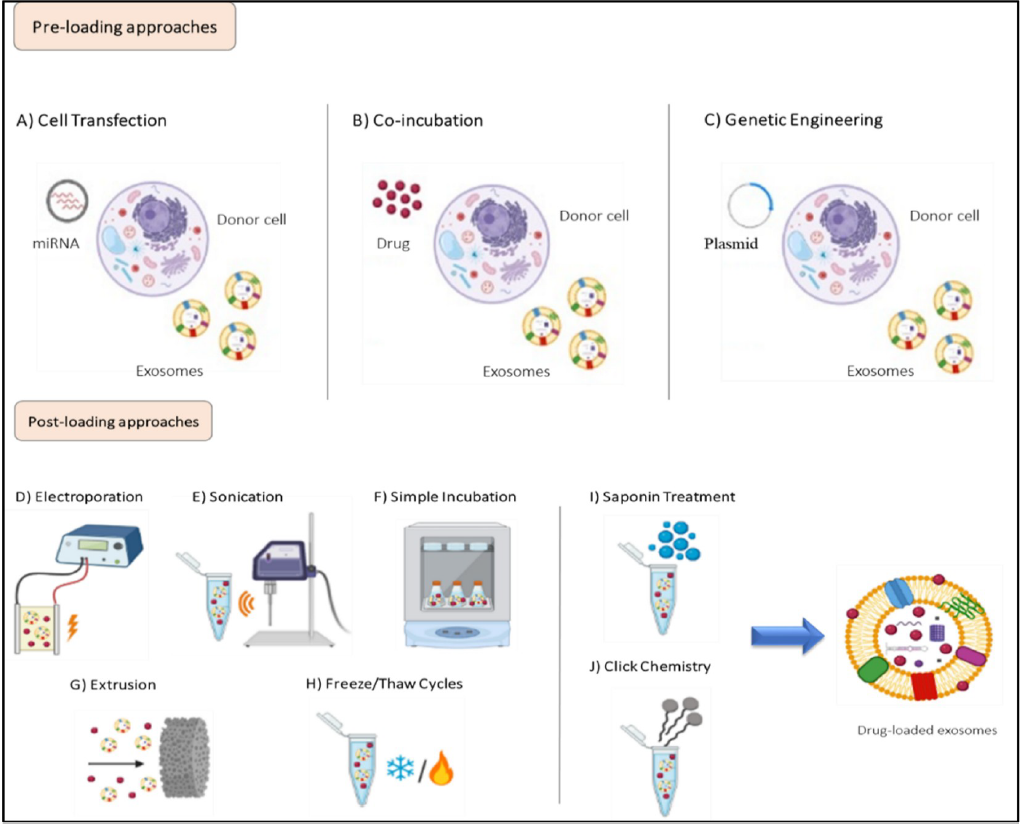
Figure | Two ways of loading drug molecules into exosomes
【Conclusion】
Overall, exosomes are microscopic vesicles with multiple functions. They have the potential to halt disease progression and, depending on the source and their composition, may serve as an important therapy for cancer.
References
Exosomes: Small vesicles with big roles in cancer, vaccine development, and therapeutics. Bioactive Materials. Volume 10, 2022, Pages 281-294. ISSN 2452-199X. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.08.029.
s will communicate with you in detail
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
-
Phone
- Service hotline+86 400-012-6688
-
E-mail
- E-mailwangal@cytoniche.com
- TOP


 京公网安备 11010802037749号
京公网安备 11010802037749号
