An Overview of the Characteristics of 2D and 3D Culture of Stem Cells
- Categories:Company News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2022-05-17
- Views:0
(Summary description)Stem cells are the general term for primitive and unspecialized cells with self-replication function and multi-directional differentiation potential, which can regenerate various cells, tissues or organs of the human body under specific conditions, and are known as "universal cells" in the medical field. Stem cells are of great significance in basic research and translational medicine applications, and have broad application prospects in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, drug screening, and precision medicine.
An Overview of the Characteristics of 2D and 3D Culture of Stem Cells
(Summary description)Stem cells are the general term for primitive and unspecialized cells with self-replication function and multi-directional differentiation potential, which can regenerate various cells, tissues or organs of the human body under specific conditions, and are known as "universal cells" in the medical field. Stem cells are of great significance in basic research and translational medicine applications, and have broad application prospects in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, drug screening, and precision medicine.
- Categories:Company News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2022-05-17
- Views:0
Stem cells are the general term for primitive and unspecialized cells with self-replication function and multi-directional differentiation potential, which can regenerate various cells, tissues or organs of the human body under specific conditions, and are known as "universal cells" in the medical field. Stem cells are of great significance in basic research and translational medicine applications, and have broad application prospects in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, drug screening, and precision medicine.

【Method of Stem Cell Culture】
At present, the culture modes of stem cells include two-dimensional (traditional) culture and three-dimensional culture.
2D (traditional) Culture:
It means that stem cells are immersed in the culture medium, and grow along the two-dimensional plane on the surface of ordinary glass or plastic culture flasks.
3D Culture:
It is to co-culture stem cells with a three-dimensional scaffold material to form a three-dimensional cell & carrier complex, allowing the stem cells to grow, proliferate and migrate in a three-dimensional space.
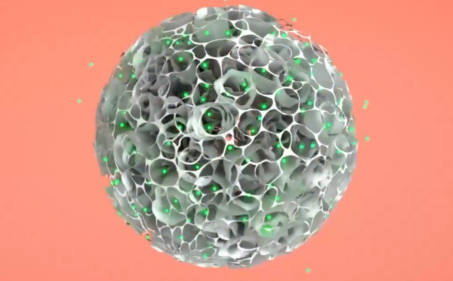
Figure: 3D Cell Culture with 3D TableTrix® Microcarriers
【Advantages of 2D and 3D Stem Cell Culture】
2D (traditional) Culture:
1. Long-established, with mature technology.
2. Simple and easy to operate.
3. Visually observe the cell state. During two-dimensional stem cell culture, the cells can be directly observed for a long time under relatively simple conditions (through an inverted microscope).
4. Used for direct differentiation of stem cells into a variety of specific cells, including chondrocytes, osteoblasts, adipocytes, cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells and hepatocytes.
3D Culture:
1. Better mimic the growth environment of cells in vivo. It can more closely mimic the complex interaction between cells and tissues and the microenvironment in vivo, providing a suitable microenvironment for optimal cell growth and differentiation. It also enables the formation of tissue-like structures in vitro.
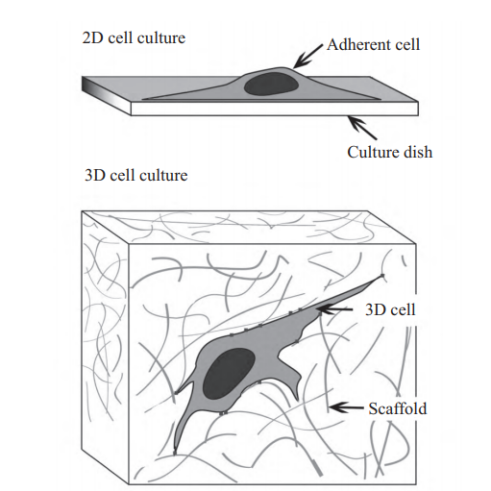
Figure: 3D cell culture model [1]
2. Stem cells cultured in three dimensions feature a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, significantly enhanced differentiation ability, and increased expression of chemokines[1].
3. Suitable for directed differentiation of stem cells. Three-dimensional culturing of cells with bioinductive, biodegradable, and biocompatible polymers mimicking the extracellular matrix, dimensionality, and spatial gradients found in natural microenvironments not only facilitates expansion and functional improvement, but is also suitable for specific differentiation of stem cells.
4. Enhance the stemness of MSCs. Relevant studies have shown that two-dimensional (traditional) stem cell culture cannot replicate the real in vivo microenvironment, resulting in a decrease in stemness during long-term culture. The stemness of some MSCs is stronger in 3D culture than in 2D culture [2].
5. Easy to achieve large-scale production and culture. At present, microsphere carriers are mostly used as scaffolds in three-dimensional culture, and the assembly of structures is realized by using scaffolds, which are micro-tissue cell scaffolds with low price and simple operation.
6. When combined with the supporting bioreactor, it is easier to control and monitor the microenvironmental parameters (temperature, aeration strategy, pH and DO changes, etc.) of growing cells to a certain extent. At the same time, with the help of online viable cell monitoring and counting, it reduces the tedious operations of sampling and the risk of bacterial contamination, thus improving cell productivity and ensuring cell quality.
【Conclusion】
The Exploration Never Stops
The two-dimensional culture mode is relatively simple and tends to be mature. Although the two-dimensional (traditional) stem cell culture method can effectively expand, it still cannot maintain the original cell characteristics of stem cells for a long time. Moreover, this culture method cannot accurately describe and mimic the rich environment and complex processes in vivo, such as signal transduction and spatial structure changes. Therefore, data collected with 2D cell culture method may be misleading for prediction of their in vivo applications.
As a whole
• The proliferation rate of cells in 3D culture may be faster or slower than that in 2D culture, and this proliferation rate is closer to the that of cells in vivo;
• 3D culture can better mimic in vivo cell morphology and physiology: The response of 3D cultured cells to drugs and physicochemical stimuli will be closer to that of cells in physiological state in vivo, and different characteristics of the microenvironment can be independently assessed to regulate tissue organogenesis and diseases, etc.;
• 3D cell culture allows us to study complex biological mechanisms, such as how osteoblasts are induced to become osteocytes, and this research process is reproducible;
• When the large-scale cell culture is required, the cost of space, labor, reagents, consumables and time for 3D cultured stem cells is much lower than that of 2D culture.
Strategic Choice
CytoNiche focuses on creating an original 3D cell "intelligent manufacturing" platform, as well as providing overall solutions for the large-scale, customized cell expansion process based on 3D microcarriers, which is the best market practice of the above research conclusions.
The stem cell three-dimensional culture technology combining three-dimensional culture and biological materials can realize the large-scale culture of stem cells, and can even be applied to the research of in vitro organoid formation, which accelerates the development of artificial organs. All this shows that 3D culture technology will be more and more favored by technology and capital market!
References:
[1] Zhao Diandian, Hou Lingling, Zhang Jingsi, Hu Honggang, Yan Qiong. The Development of Three-dimensional Cell Culture Technology and Its Application in Stem Cells and Tumor Cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2015, 37(08): 1140-1150.
[2] Li Lili. Effects of Different Dimensions of Culture on the Stemness of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and its Mechanism [D]. Nanchang University. 2021. DOI: 10.27232/d.cnki.gnchu.2021.000946
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
-
Phone
- Service hotline+86 400-012-6688
-
E-mail
- E-mailwangal@cytoniche.com
- TOP


 京公网安备 11010802037749号
京公网安备 11010802037749号
